[comment]: # (mdslides presentation.md --include media) [comment]: # (The list of themes is at https://revealjs.com/themes/) [comment]: # (The list of code themes is at https://highlightjs.org/) [comment]: # (markdown: { smartypants: true }) <style type="text/css"> .reveal { font-size: 2.2em; } .reveal .code-wrapper code { white-space: pre; font-size: 2em; line-height: 1.2em; } </style> <a href="https://github.com/exit-zero-academy/DevOpsTheHardWay.git">DevOpsTheHardWay</a> These are the slides we use in class, you're welcome to explore them. Enjoy your learning journey!
# Introduction to Virtualization and Containers <img src="media/docker_intro_dockerlogo.png" width="30%">
### Today's agenda - Bare metal systems - Virtual machines - Containers - Building containers from scratch. - Introducing Docker
## Bare metal systems - Applications are typically executed directly on the OS system. - There is no "virtualized" layer, everything is running on the same environment. - This is how you usually work on your machine. 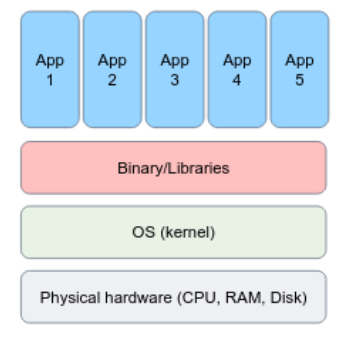
## Bare metal systems disadvantages - Dependency Conflicts - Resource Underutilization - Limited Scalability - Lack of Flexibility - High Maintenance Overhead - Limited Fault Isolation
## Virtual machines Virtual machines (VMs) are an abstraction layer that enables the creation and operation of multiple isolated instances of virtual hardware within a single physical host. - The **Hypervisor** partitions the host resources and allows each VM to have its own virtualized hardware. - **Type 1** Hypervisor is loaded directly on the hardware: [Linux KVM](https://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Main_Page), [Windows Hyper-V](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyper-v-on-windows/about/) - **Type 2** Hypervisor loaded in an OS running on the hardware: [VMwere](https://www.vmware.com/), [VirtualBox](https://www.virtualbox.org/) 
## Virtual machines 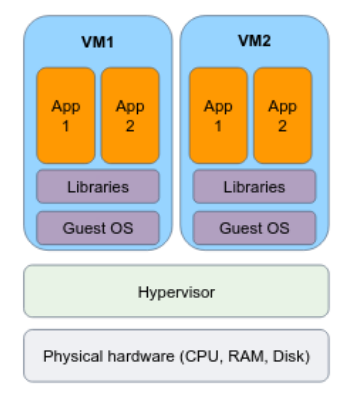
## IT Challenges Before Virtualization - Data centers are out of space - AC power panels are out of capacity - Backups are slow and expensive - Server utilization is VERY LOW - Administrators are struggling with troubleshooting - Load balancing for all applications is nearly impossible
## VMs offer several advantages - Isolation - Hardware Abstraction - Operating System Flexibility - Resource Optimization - Snapshotting and Rollbacks - Scalability and Elasticity - Migration and High Availability
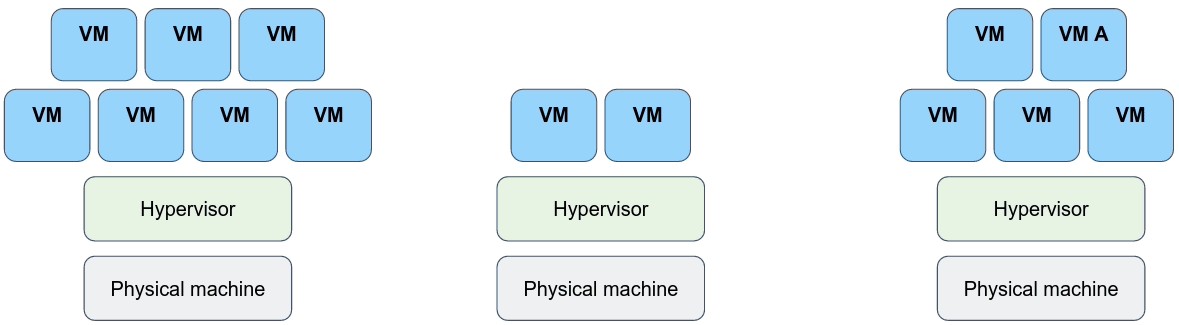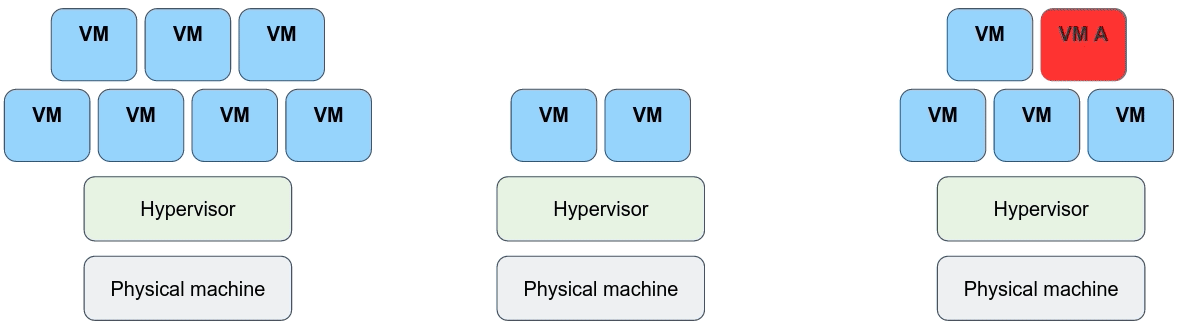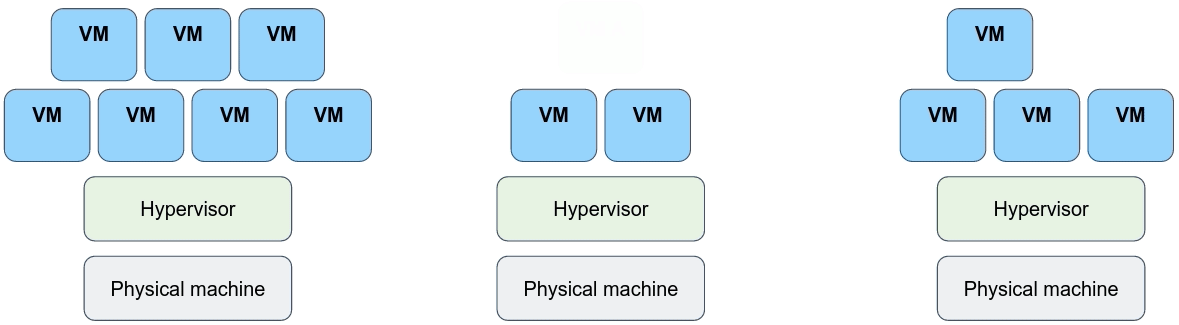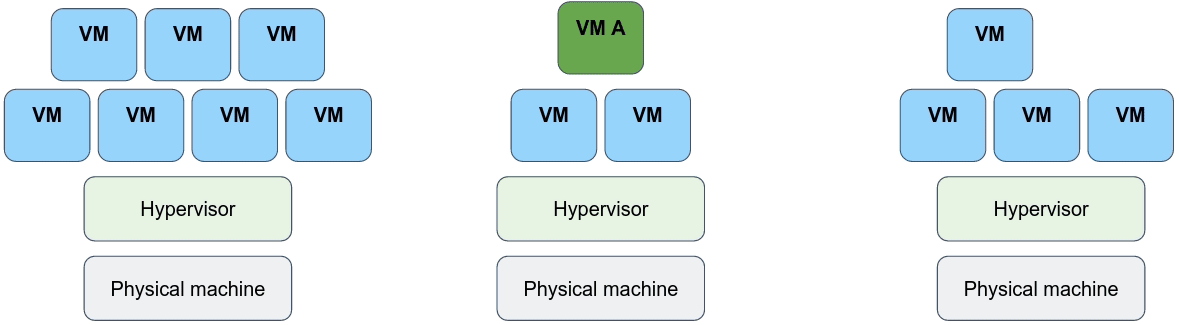
## But... The fact that every VM requires its own dedicated OS is a major flaw! Every OS consumes CPU, RAM and storage that could otherwise be used to power more applications
# Container introduced Live demo - Container from scratch https://ericchiang.github.io/post/containers-from-scratch/
## Hello Containers Instead of virtualizing at the hardware layer, containers are an abstraction at the app layer that packages code and dependencies together. - Containers utilize native Linux features like [cgroups](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cgroups) and [namespaces](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linux_namespaces) to provide isolation while **sharing the same kernel**. - This lightweight approach allows for faster startup times, improved resource efficiency, and easier scalability compared to traditional virtual machines. 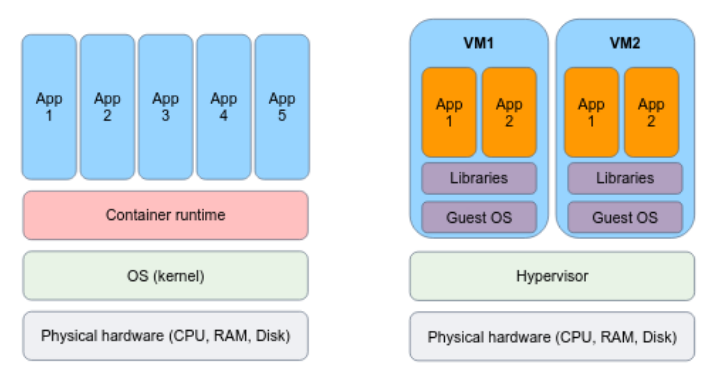
## Containers advantages - Lightweight and Portable - Isolation and Resource Efficiency - Consistent and Reproducible Builds - Scalability and Elasticity - DevOps and Continuous Integration/Deployment (CI/CD)
Under the hoods, containers are merely a **linux processes** That "lives" in an **loosely** isolated environment.
## Introducing Docker Docker is an open platform for developing, building and shipping images, and running containers. 
# Thanks